how is dka diagnosed Ketoacidosis diabetic coma non ketotic dka hhs pathogenesis clinical metabolism
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when your body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. This condition is more common in patients with type 1 diabetes, but patients with type 2 diabetes don’t have a lesser risk. The high levels of ketones in the bloodstream can cause a variety of symptoms and sometimes lead to death. If you’re living with diabetes, it’s crucial to recognize the warning signs of DKA as early as possible to get immediate medical attention. Some common symptoms of DKA include excessive thirst, frequent urination, nausea, vomiting, confusion, and difficulty breathing. To avoid developing DKA, you should regularly monitor your blood glucose levels, take your medication as prescribed, and eat a healthy, balanced diet. If you’re already experiencing symptoms of DKA, you should seek medical attention without delay. If you’re a parent of a child with type 1 diabetes, make sure to keep a close eye on their blood glucose levels and ketone levels, especially when they’re sick, as they’re at a higher risk of developing DKA. Treatment for DKA usually involves insulin therapy to lower the blood glucose levels and fluids to replace the fluids lost from excessive urination and vomiting. Electrolytes such as potassium, sodium, and chloride are also often replaced. Remember, DKA can be life-threatening if left untreated, so it’s essential to seek medical attention immediately if you’re experiencing symptoms. Prevention is key in managing diabetes and lowering the risk of developing complications like DKA. Proper management and continuous monitoring of blood glucose levels, a balanced diet, and regular exercise can significantly reduce the risk of developing this dangerous condition. In conclusion, diabetic ketoacidosis is a severe complication of diabetes that should not be taken lightly. If you’re experiencing symptoms of DKA, seek medical attention immediately. Always monitor your blood glucose levels, take your medication as prescribed, and maintain a healthy, balanced diet to lower your risk of developing this life-threatening condition.
If you are looking for Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hypersmolar Non-ketotic coma - Endocrinology you’ve visit to the right place. We have 5 Images about Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hypersmolar Non-ketotic coma - Endocrinology like Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hypersmolar Non-ketotic coma - Endocrinology, Which Disorder May Result From Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment - resultzx and also Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hypersmolar Non-ketotic coma - Endocrinology. Here you go:
Diabetic Ketoacidosis And Hypersmolar Non-ketotic Coma - Endocrinology
 www.endocrinologyadvisor.comketoacidosis diabetic coma non ketotic dka hhs pathogenesis clinical metabolism
www.endocrinologyadvisor.comketoacidosis diabetic coma non ketotic dka hhs pathogenesis clinical metabolism
SPONSORS: VCU Health CE
 thecurbsiders.comWhich Disorder May Result From Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment - Resultzx
thecurbsiders.comWhich Disorder May Result From Diabetic Ketoacidosis Treatment - Resultzx
 resultzx.blogspot.comDiabetic Ketoacidosis — What You Need To Know - Children’s National
resultzx.blogspot.comDiabetic Ketoacidosis — What You Need To Know - Children’s National
 riseandshine.childrensnational.orgketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes child childrensnational riseandshine
riseandshine.childrensnational.orgketoacidosis diabetic dka diabetes child childrensnational riseandshine
Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Symptoms, Diagnosis And Treatment | BMJ Best
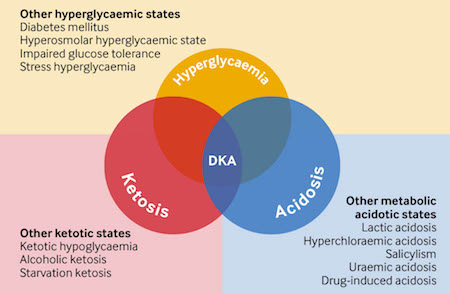 bestpractice.bmj.comdka triad ketoacidosis diabetic treatment symptoms bmj citation diagnosis am starts preceding permission adapted bm caption ae figure wall
bestpractice.bmj.comdka triad ketoacidosis diabetic treatment symptoms bmj citation diagnosis am starts preceding permission adapted bm caption ae figure wall
Diabetic ketoacidosis and hypersmolar non-ketotic coma. Sponsors: vcu health ce. Which disorder may result from diabetic ketoacidosis treatment